Machine-made sand is an indispensable material in engineering construction and plays an important role, but many users do not have a thorough understanding of machine-made sand. Here, some common knowledge of machine-made sand is introduced for your reference.
1. Definition of machine-made sand:
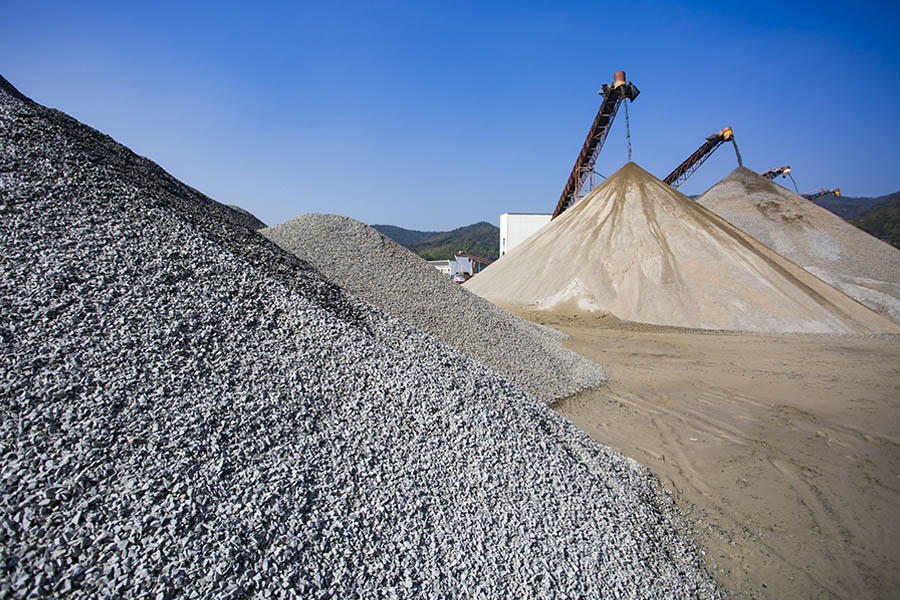
The machine-made sand refers to the rock, mine tailings or industrial waste slag particles with a particle size of less than 4.75mm made by mechanical crushing and screening after soil removal treatment. But it does not include soft, weathered particles, commonly known as artificial sand.

2. Machine-made sand specifications
According to the fineness modulus (Mx), the specifications of machine-made sand are divided into four types: coarse, medium, fine, and extra-fine, as follows:
1) Coarse sand: sand with a fineness modulus of 3.7~3.1, the content of particles larger than 0.5mm is more than 50% of the total weight, and the average particle size is 1mm~0.5mm.
2) Medium sand: sand with a fineness modulus of 3.0~2.3, the mass of particles larger than 0.25mm is more than 50% of the total weight, and the average particle size is 0.5~0.25mm.
3) Fine sand: sand with a fineness modulus of 2.2 to 1.6, particles with a particle size greater than 0.075mm exceeding 85% of the total weight, and sand with an average particle size of 0.25mm to 0.125mm.
4) Extra-fine sand: The fineness modulus is 1.5-0.7, and the average particle size is less than 0.25mm.
(Note: The larger the fineness modulus, the coarser the sand; The smaller the fineness modulus, the finer the sand.)

3. Machine-made sand processing materials

The raw materials of machine-made sand are usually granite, basalt, river stone, andesite, rhyolite, diabase, diorite, sandstone, limestone and other varieties. The machine-made sand made of it is classified according to the type of rock, and there are differences in strength and use.
4. Particle gradation of machine-made sand:
The particle gradation of sand refers to the proportion of sand-sized particles. If it is the same thickness of sand, the gap between them is larger; When the sands of two particle sizes are matched, the gap between them is reduced; The three particle sizes of sand are matched to make the smaller voids. It can be seen that the porosity of sand depends on the degree of collocation of various particle sizes of sand. Well-graded sand can not only save cement but also improve the density and strength of concrete and mortar.
6. Inspection standard of machine-made sand
The country has standardized fine aggregate inspection standards. The main inspection items are apparent relative density, firmness, mud content, sand equivalent, methylene blue value, angularity, etc,.
7. The application of machine-made sand
At present, projects with large demand for sand and gravel include subway project construction, infrastructure construction such as libraries, parks, viaducts, squares, gymnasiums, and reinforced concrete high-rise buildings, highways, railways, and bridges. Machine-made sand will be used in all industries that need to use sand, gravel, aggregates and natural sand.

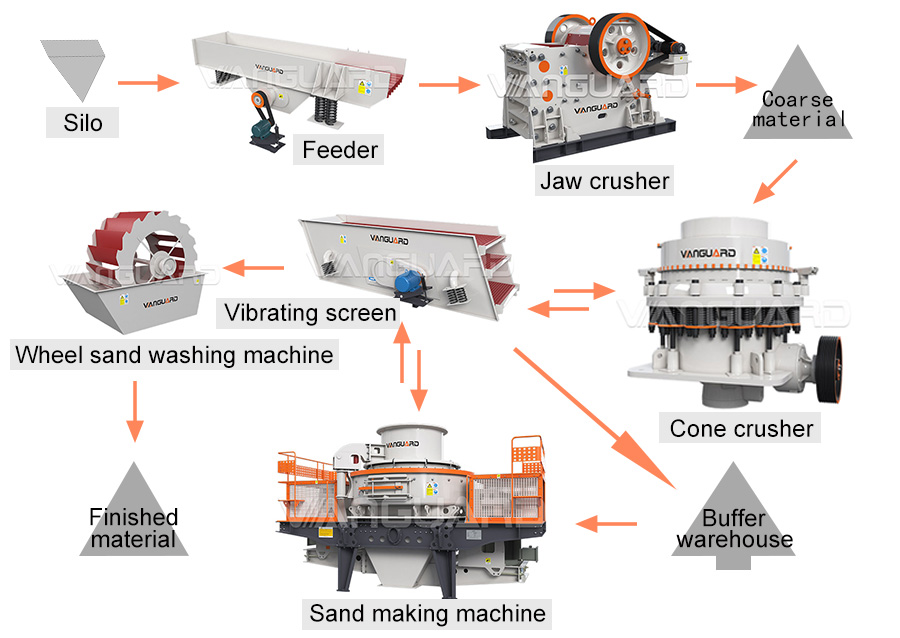
8. Production line configuration of machine-made sand
The main processing equipment of machine-made sand Production line configuration includes feeder, crusher, sand making machine, vibrating screen. It can select a suitable crusher according to the required size of the material particles. If it needs clean sand to obtain clean-finished sand, a sand washer can be equipped to clean it to remove the dust and debris mixed in the material.
9. Advantages of machine-made sand:
Quality advantages:Fixed material sources and mechanized production methods ensure the stable quality of machine-made sand and the adjustable and controllable grain size.
Grade advantages: Hard texture, low mud content, high surface energy and hydrophilicity, and complete gradation.
Resource advantage:It is not restricted by region, which can take local materials, use different ore resources and even waste resources in various places, which not only solves the problem of environmental pollution but also improves the utilization rate of natural resources.